Hyperledger fabric 1.0 代码解析 之 Process Proposal
ProcessProposal函数是chaincode调用中一个十分重要的函数,主要涉及到channel join操作,chaincode的install、deploy、upgrade、InvokeOrQuery操作等,该部分详细剖析下ProcessProposal的整个过程 1.ProcessProposal中会调用simulateProposal对chaincode进行模拟执行(callChaincode)。该过程中对于非systemChaincode需要先调用getCDFromLSCC,从system chain code lscc那里getccdata。再调用完simulateProposal之后,对于chainID非空的情况,还需要调用endorseProposal对模拟执行的结果进行背书(simulateProposal和endorseProposal同样是调用callChaincode,不过endorseProposal是将上一步simulateProposal的结果,交给escc,调用escc的Invoke进行背书)。ProcessProposal的流程大致如下图:
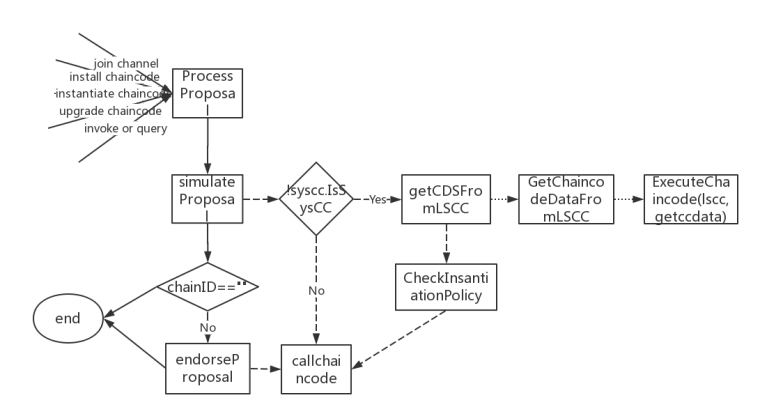
// ProcessProposal process the Proposal
func (e *Endorser) ProcessProposal(ctx context.Context, signedProp *pb.SignedProposal) (*pb.ProposalResponse, error) {
// 1. 检验消息的正确性
prop, hdr, hdrExt, err := validation.ValidateProposalMessage(signedProp)
/*一部分校验工作暂时忽略,主要是各种header的校验*/
/*禁止一些非正常的系统调用*/
chainID := chdr.ChannelId
//txid非空检查
txid := chdr.TxId
if txid == "" {
/*错误处理*/
}
endorserLogger.Debugf("processing txid: %s", txid)
/*chainID不为空,则为普通的InvokeOrQuery调用,则该部分为txid重复性检查,ACL检查等,暂时忽略*/
//获得TxSimulator和HistoryQueryExecutor,只有chainID不为空的时候需要
var txsim ledger.TxSimulator
var historyQueryExecutor ledger.HistoryQueryExecutor
if chainID != "" {//普通的InvokeOrQuery调用
if txsim, err = e.getTxSimulator(chainID); err != nil {
return &pb.ProposalResponse{Response: &pb.Response{Status: 500, Message: err.Error()}}, err
}
if historyQueryExecutor, err = e.getHistoryQueryExecutor(chainID); err != nil {
return &pb.ProposalResponse{Response: &pb.Response{Status: 500, Message: err.Error()}}, err
}
// Add the historyQueryExecutor to context
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, chaincode.HistoryQueryExecutorKey, historyQueryExecutor)
defer txsim.Done()
}
//1 -- simulate
cd, res, simulationResult, ccevent, err := e.simulateProposal(ctx, chainID, txid, signedProp, prop, hdrExt.ChaincodeId, txsim)
/*错误处理,暂时忽略*/
//2 -- endorse and get a marshalled ProposalResponse message
var pResp *pb.ProposalResponse
//chainless proposals (such as CSCC) don't have to be endorsed
if chainID == "" {
/*chainID为空则不用背书,为空的情况有channel join,chaincode的install deploy upgrade*/
pResp = &pb.ProposalResponse{Response: res}
} else {
//不为空,即普通的InvokeOrQuery,需要调用背书流程endorseProposal
pResp, err = e.endorseProposal(ctx, chainID, txid, signedProp, prop, res, simulationResult, ccevent, hdrExt.PayloadVisibility, hdrExt.ChaincodeId, txsim, cd)
/*错误处理,暂忽略*/
}
pResp.Response.Payload = res.Payload
return pResp, nil
}
core/endorser/endorser.go
//simulate the proposal by calling the chaincode
func (e *Endorser) simulateProposal(ctx context.Context, chainID string, txid string, signedProp *pb.SignedProposal, prop *pb.Proposal, cid *pb.ChaincodeID, txsim ledger.TxSimulator) (*ccprovider.ChaincodeData, *pb.Response, []byte, *pb.ChaincodeEvent, error) {
/*1. 得到chaincodeInvocationSpec,
channel join 操作,则chainID是"",chaincode是cscc,input是一个geneissblock
chaincode install,deploy,upgrade,则chainID是"",chaincode是lscc,
InvokeOrQuery操作,则chainID为channelid,chaincode为对应chaincode,input是函数名和参数等
*/
cis, err := putils.GetChaincodeInvocationSpec(prop)
/*忽略部分错误处理代码*/
var cdLedger *ccprovider.ChaincodeData
var version string
//2.如果不是systemchaincode则获得chaincodeData
if !syscc.IsSysCC(cid.Name) {
//getCCData from lscc这里其实也执行了一遍调用lscc的ExcuteChaincode
cdLedger, err = e.getCDSFromLSCC(ctx, chainID, txid, signedProp, prop, cid.Name, txsim)
/*忽略部分错误处理代码*/
version = cdLedger.Version
err = ccprovider.CheckInsantiationPolicy(cid.Name, version, cdLedger)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, nil, nil, err
}
} else {
version = util.GetSysCCVersion()
}
//3.执行proposal得到结果
res, ccevent, err := e.callChaincode(ctx, chainID, version, txid, signedProp, prop, cis, cid, txsim)
/*暂时忽略错误处理*/
if txsim != nil {
if simResult, err = txsim.GetTxSimulationResults(); err != nil {
return nil, nil, nil, nil, err
}
}
return cdLedger, res, simResult, ccevent, nil
}
//endorse the proposal by calling the ESCC
func (e *Endorser) endorseProposal(ctx context.Context, chainID string, txid string, signedProp *pb.SignedProposal, proposal *pb.Proposal, response *pb.Response, simRes []byte, event *pb.ChaincodeEvent, visibility []byte, ccid *pb.ChaincodeID, txsim ledger.TxSimulator, cd *ccprovider.ChaincodeData) (*pb.ProposalResponse, error) {
isSysCC := cd == nil
// 1) extract the name of the escc that is requested to endorse this chaincode
escc := "escc"
if !isSysCC {
escc = cd.Escc
}
// marshalling event bytes
var err error
var eventBytes []byte
if event != nil {
eventBytes, err = putils.GetBytesChaincodeEvent(event)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to marshal event bytes - %s", err)
}
}
resBytes, err := putils.GetBytesResponse(response)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to marshal response bytes - %s", err)
}
// set version of executing chaincode
if isSysCC {
ccid.Version = util.GetSysCCVersion()
} else {
ccid.Version = cd.Version
}
ccidBytes, err := putils.Marshal(ccid)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to marshal ChaincodeID - %s", err)
}
// 3) call the ESCC we've identified
// arguments:
// args[0] - function name (not used now)
// args[1] - serialized Header object
// args[2] - serialized ChaincodeProposalPayload object
// args[3] - ChaincodeID of executing chaincode
// args[4] - result of executing chaincode
// args[5] - binary blob of simulation results
// args[6] - serialized events
// args[7] - payloadVisibility
args := [][]byte{[]byte(""), proposal.Header, proposal.Payload, ccidBytes, resBytes, simRes, eventBytes, visibility}
version := util.GetSysCCVersion()
ecccis := &pb.ChaincodeInvocationSpec{ChaincodeSpec: &pb.ChaincodeSpec{Type: pb.ChaincodeSpec_GOLANG, ChaincodeId: &pb.ChaincodeID{Name: escc}, Input: &pb.ChaincodeInput{Args: args}}}
//callChaincode调用escc进行背书
res, _, err := e.callChaincode(ctx, chainID, version, txid, signedProp, proposal, ecccis, &pb.ChaincodeID{Name: escc}, txsim)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if res.Status >= shim.ERRORTHRESHOLD {
return &pb.ProposalResponse{Response: res}, nil
}
prBytes := res.Payload
//3 -- respond
pResp, err := putils.GetProposalResponse(prBytes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return pResp, nil
}
2.callchaincode是整个ProcessProposal过程中最重要的一个流程。执行过程中是通过一套状态机,通过消息变化进行的。最终调用到对应chaincode函数的Invoke或者Init函数。状态机如下:(实际上是有core/chaincode/handler.go 中也有一个FSM,在此未对其进行分析,可以自己看下) core/chaincode/shim/handler.go
v.FSM = fsm.NewFSM(
"created",
fsm.Events{
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_REGISTERED.String(), Src: []string{"created"}, Dst: "established"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_READY.String(), Src: []string{"established"}, Dst: "ready"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_ERROR.String(), Src: []string{"init"}, Dst: "established"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_RESPONSE.String(), Src: []string{"init"}, Dst: "init"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_INIT.String(), Src: []string{"ready"}, Dst: "ready"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION.String(), Src: []string{"ready"}, Dst: "ready"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_RESPONSE.String(), Src: []string{"ready"}, Dst: "ready"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_ERROR.String(), Src: []string{"ready"}, Dst: "ready"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED.String(), Src: []string{"init"}, Dst: "ready"},
{Name: pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED.String(), Src: []string{"ready"}, Dst: "ready"},
},
fsm.Callbacks{
"before_" + pb.ChaincodeMessage_REGISTERED.String(): func(e *fsm.Event) { v.beforeRegistered(e) },
"after_" + pb.ChaincodeMessage_RESPONSE.String(): func(e *fsm.Event) { v.afterResponse(e) },
"after_" + pb.ChaincodeMessage_ERROR.String(): func(e *fsm.Event) { v.afterError(e) },
//处理msg类型为ChaincodeMessage_INIT时会调用beforeInit
"before_" + pb.ChaincodeMessage_INIT.String(): func(e *fsm.Event) { v.beforeInit(e) },
//处理msg类型为ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION时会调用beforeTransaction
"before_" + pb.ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION.String(): func(e *fsm.Event) { v.beforeTransaction(e) },
},
)
详细的函数调用栈大致如下:
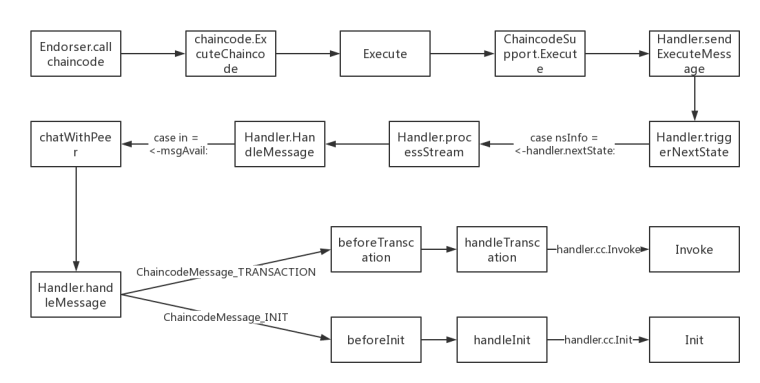 代码逐步分析如下(只关心流程的该部分请直接跳过,看上图即可):
代码逐步分析如下(只关心流程的该部分请直接跳过,看上图即可):
core/endorser/endorser.go
/*构建Context,调用chaincode的ExecuteChaincode,若是lscc需要对普通chaincode进行deploy或者upgrade操作,还需要调用chaincode的Execute函数。*/
func (e *Endorser) callChaincode(ctxt context.Context, chainID string, version string, txid string, signedProp *pb.SignedProposal, prop *pb.Proposal, cis *pb.ChaincodeInvocationSpec, cid *pb.ChaincodeID, txsim ledger.TxSimulator) (*pb.Response, *pb.ChaincodeEvent, error) {
//is this a system chaincode
scc := syscc.IsSysCC(cid.Name)
//构建chaincode的上下文环境
cccid := ccprovider.NewCCContext(chainID, cid.Name, version, txid, scc, signedProp, prop)
//执行chaincode
res, ccevent, err := chaincode.ExecuteChaincode(ctxt, cccid, cis.ChaincodeSpec.Input.Args)
/*----- BEGIN - SECTION THAT MAY NEED TO BE DONE IN LSCC ------
if this a call to deploy a chaincode, We need a mechanism to pass TxSimulator into LSCC. Till that is worked out this special code does the actual deploy, upgrade here so as to collect all state under one TxSimulator
NOTE that if there's an error all simulation, including the chaincode
table changes in lscc will be thrown away*/
if cid.Name == "lscc" && len(cis.ChaincodeSpec.Input.Args) >= 3 && (string(cis.ChaincodeSpec.Input.Args[0]) == "deploy" || string(cis.ChaincodeSpec.Input.Args[0]) == "upgrade") {
var cds *pb.ChaincodeDeploymentSpec
cds, err = putils.GetChaincodeDeploymentSpec(cis.ChaincodeSpec.Input.Args[2])
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
//禁止对systemchaincode进行install,deploy和upgrade
if syscc.IsSysCC(cds.ChaincodeSpec.ChaincodeId.Name) {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("attempting to deploy a system chaincode %s/%s", cds.ChaincodeSpec.ChaincodeId.Name, chainID)
}
cccid = ccprovider.NewCCContext(chainID, cds.ChaincodeSpec.ChaincodeId.Name, cds.ChaincodeSpec.ChaincodeId.Version, txid, false, signedProp, prop)
_, _, err = chaincode.Execute(ctxt, cccid, cds)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("%s", err)
}
return res, ccevent, err
}
core/chaincode/chaincodeexcc.go
/*构建构建ChaincodeInvocationSpec的实例,调用Execute,经过这一步调用的Execute,spec应该是ChaincodeInvocationSpec的实例*/
func ExecuteChaincode(ctxt context.Context, cccid *ccprovider.CCContext, args [][]byte) (*pb.Response, *pb.ChaincodeEvent, error) {
//构建ChaincodeInvocationSpec的实例
spec, err := createCIS(cccid.Name, args)
res, ccevent, err := Execute(ctxt, cccid, spec)
/*错误处理,省略*/
return res, ccevent, err
}
core/chaincode/exectransaction.go
/*Lanuch Chaincode, createCCMessage,调用theChaincodeSupport.Execute*/
func Execute(ctxt context.Context, cccid *ccprovider.CCContext, spec interface{}) (*pb.Response, *pb.ChaincodeEvent, error) {
//init will call the Init method of a on a chain
/*此处的spec,若是上一步ExecuteChaincode调用的,则是ChaincodeInvocationSpec的实例,则cctyp为pb.ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION;
若是由callChaincode那一步lscc的情况直接调用的Execute则为ChaincodeDeploymentSpec的实例,则cctype为ChaincodeMessage_INIT*/
cctyp := pb.ChaincodeMessage_INIT
if cds, _ := spec.(*pb.ChaincodeDeploymentSpec); cds == nil {
if ci, _ := spec.(*pb.ChaincodeInvocationSpec); ci == nil {
panic("Execute should be called with deployment or invocation spec")
}
cctyp = pb.ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION
}
//Lauch Chaincode,完成进行callchaincode之前的各项初始化操作
_, cMsg, err := theChaincodeSupport.Launch(ctxt, cccid, spec)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("%s", err)
}
var ccMsg *pb.ChaincodeMessage
ccMsg, err = createCCMessage(cctyp, cccid.TxID, cMsg)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to transaction message(%s)", err)
}
//chaincode_support调用Execute函数
resp, err := theChaincodeSupport.Execute(ctxt, cccid, ccMsg, theChaincodeSupport.executetimeout)
/*省略错误处理的情况*/
//最后消息为ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED为chaincode Invoke完成
if resp.Type == pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED {
res := &pb.Response{}
unmarshalErr := proto.Unmarshal(resp.Payload, res)
if unmarshalErr != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to unmarshal response for (%s): %s", cccid.TxID, unmarshalErr)
}
// Success
return res, resp.ChaincodeEvent, nil
}
}
core/chaincode/chaincode_support.go
// Execute executes a transaction and waits for it to complete until a timeout value.
func (chaincodeSupport *ChaincodeSupport) Execute(ctxt context.Context, cccid *ccprovider.CCContext, msg *pb.ChaincodeMessage, timeout time.Duration) (*pb.ChaincodeMessage, error) {
canName := cccid.GetCanonicalName()
chaincodeLogger.Debugf("chaincode canonical name: %s", canName)
/*省略这部分是否Lanuch的检查*/
//调用handler发送执行消息
if notfy, err := chrte.handler.sendExecuteMessage(ctxt, cccid.ChainID, msg, cccid.SignedProposal, cccid.Proposal); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Error sending %s: %s", msg.Type.String(), err)
}
var ccresp *pb.ChaincodeMessage
select {
case ccresp = <-notfy:
case <-time.After(timeout):
err = fmt.Errorf("Timeout expired while executing transaction")
}
//our responsibility to delete transaction context if sendExecuteMessage succeeded
chrte.handler.deleteTxContext(msg.Txid)
return ccresp, err
}
core/chaincode/handler.go
func (handler *Handler) sendExecuteMessage(ctxt context.Context, chainID string, msg *pb.ChaincodeMessage, signedProp *pb.SignedProposal, prop *pb.Proposal) (chan *pb.ChaincodeMessage, error) {
txctx, err := handler.createTxContext(ctxt, chainID, msg.Txid, signedProp, prop)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
//ChaincodeMessage的prop内容信息设置
if err = handler.setChaincodeProposal(signedProp, prop, msg); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
//触发执行下一步状态
handler.triggerNextState(msg, true)
return txctx.responseNotifier, nil
}
core/chaincode/handler.go
func (handler *Handler) processStream() error {
defer handler.deregister()
msgAvail := make(chan *pb.ChaincodeMessage)
var nsInfo *nextStateInfo
var in *pb.ChaincodeMessage
var err error
recv := true
//catch send errors and bail now that sends aren't synchronous
errc := make(chan error, 1)
for {
in = nil
err = nil
nsInfo = nil
if recv {
recv = false
go func() {
var in2 *pb.ChaincodeMessage
in2, err = handler.ChatStream.Recv()
msgAvail <- in2
}()
}
select {
case sendErr := <-errc:
/*errc情况,暂时忽略该部分内容*/
case in = <-msgAvail:
/*msgAvail情况,暂时忽略该部分内容*/
case nsInfo = <-handler.nextState:
/*上一步的triggerNextState,会触发这一步*/
in = nsInfo.msg
if in == nil {
/*错误处理*/
}
chaincodeLogger.Debugf("[%s]Move state message %s", shorttxid(in.Txid), in.Type.String())
case <-handler.waitForKeepaliveTimer():
/*暂时忽略该部分*/
}
//处理in得到的消息,这里主要是状态机的处理,不过该处的状态机不同于上一部分给出的状态机,不过这个时候Event里并没有什么操作,可以暂时忽略此处状态机的结构
err = handler.HandleMessage(in)
/*错误处理*/
//这边会把in的信息send
if nsInfo != nil && nsInfo.sendToCC {
chaincodeLogger.Debugf("[%s]sending state message %s", shorttxid(in.Txid), in.Type.String())
//ready messages are sent sync
if nsInfo.sendSync {
if in.Type.String() != pb.ChaincodeMessage_READY.String() {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("[%s]Sync send can only be for READY state %s\n", shorttxid(in.Txid), in.Type.String()))
}
if err = handler.serialSend(in); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("[%s]Error sending ready message, ending stream: %s", shorttxid(in.Txid), err)
}
} else {
//if error bail in select
handler.serialSendAsync(in, errc)
}
}
}
}
core/chaincode/handler.go
// HandleMessage implementation of MessageHandler interface. Peer's handling of Chaincode messages.
func (handler *Handler) HandleMessage(msg *pb.ChaincodeMessage) error {
/*COMPLETED的处理,这个是TRANSCATION或者INIT处理完后再触发下一状态的时候会运行的地方,会调用notify*/
if (msg.Type == pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED || msg.Type == pb.ChaincodeMessage_ERROR) && handler.FSM.Current() == "ready" {
chaincodeLogger.Debugf("[%s]HandleMessage- COMPLETED. Notify", msg.Txid)
handler.notify(msg)
return nil
}
//这里的msg.Type是ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION or ChaincodeMessage_INIT
//这里的状态机并不会对这两种情况进行操作
eventErr := handler.FSM.Event(msg.Type.String(), msg)
filteredErr := filterError(eventErr)
if filteredErr != nil {
chaincodeLogger.Errorf("[%s]Failed to trigger FSM event %s: %s", msg.Txid, msg.Type.String(), filteredErr)
}
return filteredErr
}
core/chaincode/shim/chaincode.go
func chatWithPeer(chaincodename string, stream PeerChaincodeStream, cc Chaincode) error {
// Create the shim handler responsible for all control logic
handler := newChaincodeHandler(stream, cc)
defer stream.CloseSend()
/*忽略掉一部分检查和错误处理的内容*/
waitc := make(chan struct{})
errc := make(chan error)
go func() {
defer close(waitc)
msgAvail := make(chan *pb.ChaincodeMessage)
var nsInfo *nextStateInfo
var in *pb.ChaincodeMessage
recv := true
for {
in = nil
err = nil
nsInfo = nil
if recv {
recv = false
go func() {
var in2 *pb.ChaincodeMessage
//这边会收到上一步processStream里send的消息
in2, err = stream.Recv()
msgAvail <- in2
}()
}
select {
/暂时忽略其他情况,以免误导*/
case in = <-msgAvail:
/*各种错误处理,从processItem调用之后,是先到这里(那边send的消息)*/
shorttxid(in.Txid), in.Type.String())
recv = true
}
// Call FSM.handleMessage()
err = handler.handleMessage(in)
if err != nil {
err = fmt.Errorf("Error handling message: %s", err)
return
}
//keepalive messages are PONGs to the fabric's PINGs
if in.Type == pb.ChaincodeMessage_KEEPALIVE {
chaincodeLogger.Debug("Sending KEEPALIVE response")
handler.serialSendAsync(in, nil)
} else if nsInfo != nil && nsInfo.sendToCC {
//该部分会将COMPLETED的消息返回回去,
handler.serialSendAsync(in, errc)
}
}
}()
<-waitc
return err
}
core/chaincode/shim/chaincode.go
// handleMessage message handles loop for shim side of chaincode/validator stream.
func (handler *Handler) handleMessage(msg *pb.ChaincodeMessage) error {
/*忽略掉其他情况和错误处理*/
/这里msg.Type是ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION or ChaincodeMessage_INIT,Event处理的时候会调用相应的callback,即beforeTransaction or beforeInit*/
err := handler.FSM.Event(msg.Type.String(), msg)
return filterError(err)
}
core/chaincode/shim/chaincode.go
// beforeTransaction will execute chaincode's Run if coming from a TRANSACTION event.
func (handler *Handler) beforeTransaction(e *fsm.Event) {
/*忽略掉错误处理*/
if msg.Type.String() == pb.ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION.String() {
// Call the chaincode's Run function to invoke transaction
handler.handleTransaction(msg)
}
}
core/chaincode/shim/chaincode.go
// handleTransaction Handles request to execute a transaction.
func (handler *Handler) handleTransaction(msg *pb.ChaincodeMessage) {
go func() {
defer func() {
handler.triggerNextState(nextStateMsg, send)
}()
/*忽略掉错误处理,以及一些辅助内容*/
//调用chaincode的Invoke函数,joinchannel的时候是cscc的Invoke
res := handler.cc.Invoke(stub)
/*.....*/
//完成Invoke,nextState为COMPLETED
nextStateMsg = &pb.ChaincodeMessage{Type: pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED, Payload: resBytes, Txid: msg.Txid, ChaincodeEvent: stub.chaincodeEvent}
}()
}
// beforeInit will initialize the chaincode if entering init from established.
func (handler *Handler) beforeInit(e *fsm.Event) {
/*忽略掉错误处理*/
if msg.Type.String() == pb.ChaincodeMessage_INIT.String() {
// Call the chaincode's Run function to initialize
handler.handleInit(msg)
}
}
// handleInit handles request to initialize chaincode.
func (handler *Handler) handleInit(msg *pb.ChaincodeMessage) {
go func() {
var nextStateMsg *pb.ChaincodeMessage
send := true
defer func() {
handler.triggerNextState(nextStateMsg, send)
}()
/*忽略掉错误处理,以及一些辅助内容*/
// Call chaincode's Run
// Create the ChaincodeStub which the chaincode can use to callback
stub := new(ChaincodeStub)
err := stub.init(handler, msg.Txid, input, msg.Proposal)
if nextStateMsg = errFunc(err, nil, stub.chaincodeEvent, "[%s]Init get error response [%s]. Sending %s", shorttxid(msg.Txid), pb.ChaincodeMessage_ERROR.String()); nextStateMsg != nil {
return
}
res := handler.cc.Init(stub)
/*.....*/
// Send COMPLETED message to chaincode support and change state
nextStateMsg = &pb.ChaincodeMessage{Type: pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED, Payload: resBytes, Txid: msg.Txid, ChaincodeEvent: stub.chaincodeEvent}
chaincodeLogger.Debugf("[%s]Init succeeded. Sending %s", shorttxid(msg.Txid), pb.ChaincodeMessage_COMPLETED)
}()
}
3.调用到相应的Invoke或者Init函数之后,会返回COMPLETED,COMPLETED消息也会在状态机中进行相应的处理,最终将消息传递回最初的调用者。该部分不在这里一一详述了。